- Call Us: 011 4652 8024
- Email: info@pushpanjalihospitals.com

When one gets hospitalized because of severe medical conditions, doctors may prescribe special care units such as ICU, HDU, or NICU. All three units are specially designed to provide different levels of medical care depending on the situation of the patient. Becoming familiar with the difference between ICU HDU NICU will allow you to make rational choices during hectic moments.
In this guide, we’ll break down what each unit means, the type of care provided, and when a patient might need admission to one of these critical care units.
Before comparing them, let’s define each unit clearly.
The definition of ICU is a hospital ward with intensive care for seriously ill patients. An ICU hospital in Delhi involves continuous monitoring, advanced medical equipment, and a higher ratio of doctors and nurses to patients.
The indications for admission to the ICU are:
Severe infections or sepsis
Surgical complications
Cardiac arrest or respiratory failure
Trauma or major injury
The High Dependency Unit is a level below ICU but provides more assistance than a general ward. People who are no longer severely ill but still require close monitoring are cared for here, typically at an HDU hospital in Delhi.
HDU care requires:
Oxygen therapy
Monitoring of the heart
Post-op recovery with risk of complication
Stable patients but not yet ready for general ward
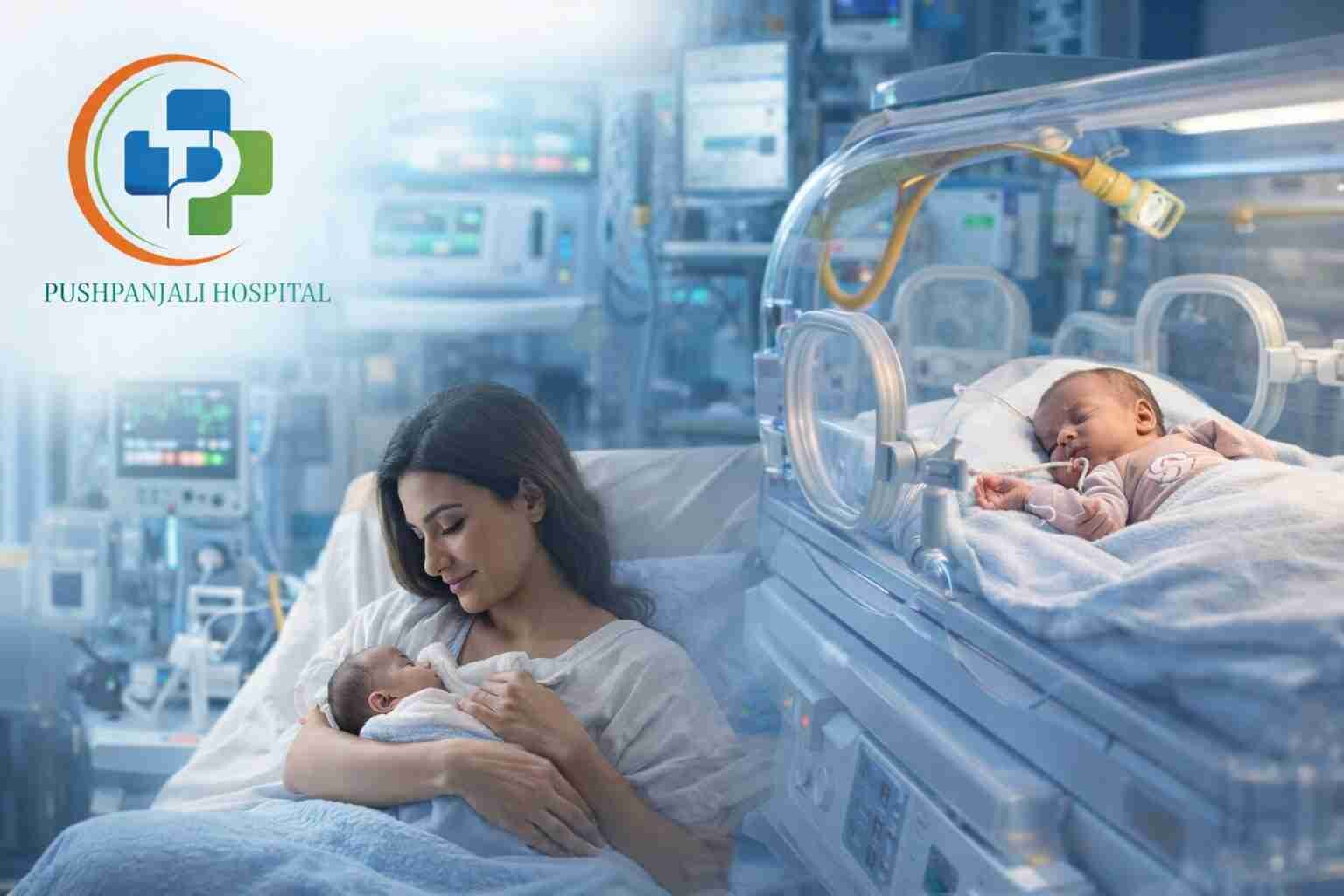
Neonatal Intensive Care Unit is where the new-born babies get specialized medical care. They can be premature babies, low birth weight babies, or sick babies.
NICU baby care involves:
Incubators to warm them up
Ventilator support to help breathe for them
Feeding tubes to feed them
Constant monitoring of vitals
Although all three are intensive care units, each operates with a different kind of patient and provides different care.
ICU is for critically ill patients of any age with a need for high-level and rapid care.
HDU is for stable patients still at risk and in need of close observation before they can be moved to a general ward.
NICU is for neonates requiring intensive specialist neonatal treatment such as premature babies or babies with complications during delivery.
Families often ask about the difference between HDU and ICU. It depends on the degree of monitoring and illness severity.
ICU patients are unstable and may be on ventilators, dialysis, or life support machines. They are under constant monitoring from a huge team of specialists.
HDU patients are stable but not cured. They require oxygen supply, heart monitoring, and medicine but seldom need life support.
ICU beds are provided with state-of-the-art equipment like ventilators, infusion pumps, and dialysis machines.
HDU beds provide monitoring and oxygen therapy but with reduced equipment and reduced staffing.
As ICU care involves additional staff and equipment, these wards usually contain fewer beds than HDUs, which accept more patients at once.
If a newborn experiences health issues, physicians can suggest admission to the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU).
Infants are usually admitted to NICU due to:
Premature birth (prior to 37 weeks)
Low birth weight
Respiratory distress
Infections or congenital abnormalities
Neonatal ICU treatment offers incubators, ventilators, specialized nutrition, and continuous monitoring. Such neonatal care units, like those at a NICU hospital in Delhi, are attended by neonatologists and nurses who provide care exclusively to infants.
Simply put:
ICU provides the highest degree of care for severely ill patients of all ages.
HDU is the middle stage between ICU and general ward for those patients who are on the way to recovery but are not stabilized yet.
NICU is saved for babies who need special medical intervention.
All these types of critical care units play different roles to provide the patient with the right care according to their illness.
The entry of an individual into ICU or HDU is determined by doctors, but the following are some common guidelines:
ICU entry: Required for unstable patients, ventilator-dependent, or constantly in need of life support.
HDU entry: Recommended for stable patients who need intensive monitoring, for example, after a major surgery or recovering from a serious illness.
For newborns, a comparison of ICU and NICU does not apply since NICU is infant-only specialized care.
Staffing and services are one of the differences:
ICU staff vs HDU staff: ICU has more staff per patient with physicians, nurses, and respiratory therapists available continuously. HDU has fewer per patient but maintains specialized monitoring.
HDU services: Cover oxygen therapy, medication control, and recovery for patients not critically ill enough for ICU.
Both ICU and NICU are very specialized but treat different groups:
ICU cares for adults and children with life-threatening illnesses.
NICU delivers neonatal intensive care to premature or unwell newborn babies.
Both units use advanced technology, constant monitoring, and highly skilled teams despite serving different patients.
Also Read: How ICU Hospitals in Delhi Are Minimizing Risks and Enhancing Outcomes in Critical Care
Having knowledge of the difference between ICU, HDU, and NICU allows families to prepare for the type of medical treatment their relative might need.
ICU is for patients in critical, life-threatening condition.
HDU is for stable patients who need to be monitored closely.
NICU is for newborn babies who need neonatal specialists.
Every unit ensures patients get the right care at the right time. If ever you are in a similar situation, do not hesitate to ask the medical team to further explain the level of care.
Would you like to learn more about specialized hospital care? Get in touch with us to talk care options and receive personalized advice tailored to your needs.